opencv+python机读卡识别(进阶版)
在 上一篇文章(初级版) 中,我们初步介绍了扫描机读卡的识别,
在这篇文章中,我们进一步机读卡的识别,
在这里,我们使用高拍仪的图片进行识别,
进一步讲解封装类库,如何打开文件夹,获取文件目录,
边缘检测、四点变化裁切、识别结果保存excel等操作。
当然,熟悉相关业务流程可直接跳过流程,看(最终版),
本地使用环境(win10 64位,python3.7)
一、读取相对目录文件(获选则读取目录)
import os
import re
from tkinter import filedialog
import win32api,win32con
class cardReading(object):
# 获取目录下的文件
def print_all_file_path(self, init_file_path, keyword='jpg'):
url = []
for cur_dir, sub_dir, included_file in os.walk(init_file_path):
if included_file:
for file in included_file:
if re.search(keyword, file):
url.append(cur_dir + "/" + file)
return url
if __name__=="__main__":
cardReading = cardReading()
url = cardReading.print_all_file_path("./card");
url = [];
if len(url) == 0:
Folderpath = filedialog.askdirectory() # 获得选择好的文件夹
url = cardReading.print_all_file_path(Folderpath);
print(url)
if len(url) > 0:
for x in range(0,len(url)):
print(url[x])
else:
win32api.MessageBox(0, "未选择识别目录", "提醒", win32con.MB_OK)
二、循环文件,进行图片的初步操作(灰阶,轻度模糊,二值化处理)
1、从选择的目录下的文件进行,循环识别操作
if len(url) > 0:
for x in range(0,len(url)):
# print(url[x])
aaaa = cardReading.reading(url[x], x)
print(aaaa)
else:
win32api.MessageBox(0, "未选择识别目录", "提醒", win32con.MB_OK)
2、加载图片,将它转换为灰阶,轻度模糊,然后二值化处理。
class cardReading(object):
# 机读卡信息读取
def reading(self, url, count):
# 加载图片,将它转换为灰阶,轻度模糊,然后边缘检测。
image = cv2.imread(url)
#转换为灰度图像
gray = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
#高斯滤波
blurred = cv2.GaussianBlur(gray, (7, 7), 0)
#自适应二值化方法
blurred=cv2.adaptiveThreshold(blurred,255,cv2.ADAPTIVE_THRESH_MEAN_C,cv2.THRESH_BINARY,51,2)
三、识别图像边缘,找出四点,进行四点变换的图像裁切
图像裁切的目的是将图像定个便于识别的样子(类似上篇中的扫描图),
比如这里四角变换结束以后会吧图像变为5000*7000的大小,
无论是什么样的案例图片,都是这个格式,这样最后在局部分割,
如选择题答案的识别和学号的确定这套程序才能有较好的通用性。
1、图像边缘识别
edged = cv2.Canny(blurred, 75, 200)
# 从边缘图中寻找轮廓,然后初始化答题卡对应的轮廓
'''
findContours
image -- 要查找轮廓的原图像
mode -- 轮廓的检索模式,它有四种模式:
cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL 表示只检测外轮廓
cv2.RETR_LIST 检测的轮廓不建立等级关系
cv2.RETR_CCOMP 建立两个等级的轮廓,上面的一层为外边界,里面的一层为内孔的边界信息。如果内孔内还有一个连通物体,这个物体的边界也在顶层。
cv2.RETR_TREE 建立一个等级树结构的轮廓。
method -- 轮廓的近似办法:
cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE 存储所有的轮廓点,相邻的两个点的像素位置差不超过1,即max (abs (x1 - x2), abs(y2 - y1) == 1
cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE压缩水平方向,垂直方向,对角线方向的元素,只保留该方向的终点坐标,例如一个矩形轮廓只需4个点来保存轮廓信息
cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_TC89_L1,CV_CHAIN_APPROX_TC89_KCOS使用teh-Chinl chain 近似算法
'''
cnts = cv2.findContours(edged, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL,cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
cnts = cnts[1] if imutils.is_cv3() else cnts[0]
docCnt = None
# 确保至少有一个轮廓被找到
if len(cnts) > 0:
# 将轮廓按大小降序排序
cnts = sorted(cnts, key=cv2.contourArea, reverse=True)
# 对排序后的轮廓循环处理
for c in cnts:
# 获取近似的轮廓
peri = cv2.arcLength(c, True)
approx = cv2.approxPolyDP(c, 0.02 * peri, True)
# 如果近似轮廓有四个顶点,那么就认为找到了答题卡
if len(approx) == 4:
docCnt = approx
break
2、顶点坐标处理
因本示例右下角图片不规则,所以需要第一步处理,如果图片规则,可忽略当前操作
# 对右下角坐标点进行处理
bottom_left = bottom_right = None
for x in range(0, len(docCnt)):
doc = list(docCnt[x][0]);
doc.append(x)
if doc[0] < 1000 and doc[1] > 1500:
bottom_left = doc
if doc[0] > 1000 and doc[1] > 1500:
bottom_right = doc
if bottom_left is not None and bottom_right is not None:
if abs(bottom_right[1] - bottom_left[1]) > 70:
docCnt[bottom_right[2]][0][1] = bottom_right[1] + 70
else:
docCnt[bottom_right[2]][0][0] = bottom_right[0] + 70
第二步操作(必须)
newimage=image.copy()
for i in docCnt:
#circle函数为在图像上作图,新建了一个图像用来演示四角选取
cv2.circle(newimage, (i[0][0],i[0][1]), 50, (255, 0, 0), -1)
3、四点变换,直接调用 four_point_transform
paper = four_point_transform(image, docCnt.reshape(4, 2))
warped = four_point_transform(gray, docCnt.reshape(4, 2))
四、对整张机读卡,学号和选择题图像部分预处理
# 对灰度图应用二值化算法
thresh=cv2.adaptiveThreshold(warped,255,cv2.ADAPTIVE_THRESH_MEAN_C,cv2.THRESH_BINARY,53,2)
threshtmmp=thresh
thresh = cv2.resize(thresh, (5000, 7000), cv2.INTER_LANCZOS4)
fImage = cv2.resize(paper, (5000, 7000), cv2.INTER_LANCZOS4)
# paper 用来标记边缘检测,所以建一个来保存
paperorign = paper
warped = cv2.resize(warped, (5000, 7000), cv2.INTER_LANCZOS4)
ChQImg = cv2.blur(thresh, (40, 40))
ChQImg = cv2.threshold(ChQImg, 25, 225, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)[1]
五、寻找结果中黑块坐标
# 在二值图像中查找轮廓
cnts = cv2.findContours(ChQImg, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
cnts = cnts[1] if imutils.is_cv3() else cnts[0]
questionCnts = []
Answer = []
for c in cnts:
# 计算轮廓的边界框,然后利用边界框数据计算宽高比
(x, y, w, h) = cv2.boundingRect(c)
if ((y>3320 and y<5400) or (y>2090 and y<3100)) and x > 400 and x < 4730 and w > 60 and h > 20:
M = cv2.moments(c)
cX = int(M["m10"] / M["m00"])
cY = int(M["m01"] / M["m00"])
#绘制中心及其轮廓
cv2.drawContours(fImage, c, -1, (0, 0, 255), 5, lineType=0)
cv2.circle(fImage, (cX, cY), 7, (255, 255, 255), -1)
#保存题目坐标信息
Answer.append((cX, cY))

六、循环坐标计算用户学号、选择题题号及答案
1、将学号坐标与选择题坐标区分开来
# 学号相关坐标系
xt0=[0,688,1120,1570,2005,1450,2890,3340,3783,4240,4680,5000]
yt0=[2090,2220,2320,2410,2510,2600,2705,2795,2900,2990,3100]
# 选择题相关坐标系
xt1=[0,550,715,860,1016,1165,1435,1585,1735,1880,2025,2315,2455,2610,2770,2925,3075,3225,3380,3530,3700,3860,4015,4170,4325,4480,5000]
yt1=[3400,3600,3725,3845,3955,4100,4280,4390,4505,4620,4785,4935,5055,5175,5290,5450]
student = []
IDAnswer = []
for i in Answer:
# 学号坐标列表
if i[1] > yt0[0] and i[1] < yt0[-1]:
student.append(i)
# 选择题相关坐标答案计算
else :
for j in range(0,len(xt1)-1):
if i[0]>xt1[j] and i[0]<xt1[j+1]:
for k in range(0,len(yt1)-1):
if i[1]>yt1[k] and i[1]<yt1[k+1]:
option = self.judge0(j, k, i[0], i[1])
IDAnswer.append(option)
2、计算用户学号(采用冒泡排序的方法)
xuehao = '';
for i in self.bubble_sort(student):
for k in range(0,len(yt0)-1):
if i[1]>yt0[k] and i[1]<yt0[k+1]:
xuehao += str(k)
# 冒泡排序
def bubble_sort(self, list):
count = len(list)
for i in range(count):
for j in range(i + 1, count):
if list[i] > list[j]:
list[i], list[j] = list[j], list[i]
return list
3、集中处理信息,将数据进行返回
IDAnswer.sort()
newIDAnswer = {'学号':str(xuehao)}
for x in IDAnswer:
if x[0] <= 60:
if x[0] not in newIDAnswer:
answer = x[1]
else :
answer = newIDAnswer[x[0]] + x[1]
newIDAnswer[x[0]] = answer;
# print(xuehao)
# print(newIDAnswer)
return newIDAnswer
七、接收数据,保存到excel中
with open('names.csv', 'w', newline='') as csvfile:
fieldnames = list(range(1, 61))
fieldnames.insert(0,'学号')
writer = csv.DictWriter(csvfile, fieldnames=fieldnames)
writer.writeheader() # 注意有写header操作
for x in range(0,len(url)):
# print(url[x])
aaaa = cardReading.reading(url[x], x)
writer.writerow(aaaa)
print(aaaa)
if x == len(url)-1:
print('已全部读取');
for i in range(0,3):
time.sleep(1)
print('即将关闭...%2d.....' % (3-i));
完整示例代码
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# @Author: [FENG] <1161634940@qq.com>
# @Date: 2020-05-12 12:35:58
# @Last Modified by: [FENG] <1161634940@qq.com>
# @Last Modified time: 2020-05-31 10:51:59
from imutils.perspective import four_point_transform
import imutils
import cv2
import csv
import os
import re
import time
from PIL import Image
# import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import filedialog
import win32api,win32con
class cardReading(object):
# 机读卡信息读取
def reading(self, url, count):
# 加载图片,将它转换为灰阶,轻度模糊,然后边缘检测。
image = cv2.imread(url)
#转换为灰度图像
gray = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
#高斯滤波
blurred = cv2.GaussianBlur(gray, (7, 7), 0)
#自适应二值化方法
blurred=cv2.adaptiveThreshold(blurred,255,cv2.ADAPTIVE_THRESH_MEAN_C,cv2.THRESH_BINARY,51,2)
# cv2.imwrite('./%02d.jpg' % count, blurred);
blurred=cv2.copyMakeBorder(blurred,5,5,5,5,cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT,value=(255,255,255))
edged = cv2.Canny(blurred, 75, 200)
cnts = cv2.findContours(edged, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL,cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
cnts = cnts[1] if imutils.is_cv3() else cnts[0]
docCnt = None
# 确保至少有一个轮廓被找到
if len(cnts) > 0:
# 将轮廓按大小降序排序
cnts = sorted(cnts, key=cv2.contourArea, reverse=True)
# 对排序后的轮廓循环处理
for c in cnts:
# 获取近似的轮廓
peri = cv2.arcLength(c, True)
approx = cv2.approxPolyDP(c, 0.02 * peri, True)
# 如果近似轮廓有四个顶点,那么就认为找到了答题卡
if len(approx) == 4:
docCnt = approx
break
# 对右下角坐标点进行处理
bottom_left = bottom_right = None
for x in range(0, len(docCnt)):
doc = list(docCnt[x][0]);
doc.append(x)
if doc[0] < 1000 and doc[1] > 1500:
bottom_left = doc
if doc[0] > 1000 and doc[1] > 1500:
bottom_right = doc
if bottom_left is not None and bottom_right is not None:
if abs(bottom_right[1] - bottom_left[1]) > 70:
docCnt[bottom_right[2]][0][1] = bottom_right[1] + 70
else:
docCnt[bottom_right[2]][0][0] = bottom_right[0] + 70
newimage=image.copy()
for i in docCnt:
cv2.circle(newimage, (i[0][0],i[0][1]), 50, (255, 0, 0), -1)
# cv2.imwrite('./%02d.jpg' % count, newimage);
paper = four_point_transform(image, docCnt.reshape(4, 2))
warped = four_point_transform(gray, docCnt.reshape(4, 2))
# cv2.imwrite('./%02d.jpg' % count, paper);
# 对灰度图应用二值化算法
thresh=cv2.adaptiveThreshold(warped,255,cv2.ADAPTIVE_THRESH_MEAN_C,cv2.THRESH_BINARY,53,2)
threshtmmp=thresh
thresh = cv2.resize(thresh, (5000, 7000), cv2.INTER_LANCZOS4)
fImage = cv2.resize(paper, (5000, 7000), cv2.INTER_LANCZOS4)
# paper 用来标记边缘检测,所以建一个来保存
paperorign = paper
warped = cv2.resize(warped, (5000, 7000), cv2.INTER_LANCZOS4)
ChQImg = cv2.blur(thresh, (40, 40))
ChQImg = cv2.threshold(ChQImg, 25, 225, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)[1]
# 在二值图像中查找轮廓
cnts = cv2.findContours(ChQImg, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
cnts = cnts[1] if imutils.is_cv3() else cnts[0]
questionCnts = []
Answer = []
for c in cnts:
# 计算轮廓的边界框,然后利用边界框数据计算宽高比
(x, y, w, h) = cv2.boundingRect(c)
if ((y>3320 and y<5400) or (y>2090 and y<3100)) and x > 400 and x < 4730 and w > 60 and h > 20:
M = cv2.moments(c)
cX = int(M["m10"] / M["m00"])
cY = int(M["m01"] / M["m00"])
#绘制中心及其轮廓
cv2.drawContours(fImage, c, -1, (0, 0, 255), 5, lineType=0)
cv2.circle(fImage, (cX, cY), 7, (255, 255, 255), -1)
#保存题目坐标信息
Answer.append((cX, cY))
# cv2.imwrite('./%02d.jpg' % count, fImage);
xt0=[0,688,1120,1570,2005,1450,2890,3340,3783,4240,4680,5000]
yt0=[2090,2220,2320,2410,2510,2600,2705,2795,2900,2990,3100]
xt1=[0,550,715,860,1016,1165,1435,1585,1735,1880,2025,2315,2455,2610,2770,2925,3075,3225,3380,3530,3700,3860,4015,4170,4325,4480,5000]
yt1=[3400,3600,3725,3845,3955,4100,4280,4390,4505,4620,4785,4935,5055,5175,5290,5450]
student = []
IDAnswer = []
for i in Answer:
if i[1] > yt0[0] and i[1] < yt0[-1]:
student.append(i)
else :
for j in range(0,len(xt1)-1):
if i[0]>xt1[j] and i[0]<xt1[j+1]:
for k in range(0,len(yt1)-1):
if i[1]>yt1[k] and i[1]<yt1[k+1]:
option = self.judge0(j, k, i[0], i[1])
IDAnswer.append(option)
xuehao = '';
for i in self.bubble_sort(student):
for k in range(0,len(yt0)-1):
if i[1]>yt0[k] and i[1]<yt0[k+1]:
xuehao += str(k)
IDAnswer.sort()
newIDAnswer = {'学号':str(xuehao)}
for x in IDAnswer:
if x[0] <= 60:
if x[0] not in newIDAnswer:
answer = x[1]
else :
answer = newIDAnswer[x[0]] + x[1]
newIDAnswer[x[0]] = answer;
# print(xuehao)
# print(newIDAnswer)
return newIDAnswer
# 冒泡排序
def bubble_sort(self, list):
count = len(list)
for i in range(count):
for j in range(i + 1, count):
if list[i] > list[j]:
list[i], list[j] = list[j], list[i]
return list
# 图片预览
def see_img(self, image):
cv2.namedWindow("image",0);
cv2.resizeWindow("image", 480, 640);
cv2.imshow("image", image)
cv2.waitKey(0)
exit()
# 卷子model0判题
def judgey0(self, y):
if (y / 5 < 1):
return y + 1
elif y / 5 < 2 and y/5>=1:
return y % 5 + 25 + 1
else:
return y % 5 + 45 + 1
# 获取选项
def judgex(self, x, y=1):
letter = 'ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ'
return letter[x%(5*y)-1]
# 获取目录下的文件
def print_all_file_path(self, init_file_path, keyword='jpg'):
url = []
for cur_dir, sub_dir, included_file in os.walk(init_file_path):
if included_file:
for file in included_file:
if re.search(keyword, file):
url.append(cur_dir + "/" + file)
return url
# 题号与对应选项进行处理
def judge0(self, x, y, m, n):
# score = 20
if n > 4140 and n < 4800:
if x/5<1 :
num = self.judgey0(y)
elif x/5<2 and x/5>=1:
num = self.judgey0(y)+5
elif x/5<4 and x/5>=2:
num = self.judgey0(y)+10
else:
num = self.judgey0(y)+15
else:
if x/5<1 :
num = self.judgey0(y)
elif x/5<2 and x/5>=1:
num = self.judgey0(y)+5
elif x/5<3 and x/5>=2:
num = self.judgey0(y)+10
elif x/5<4 and x/5>=3:
num = self.judgey0(y)+15
else:
num = self.judgey0(y)+20
if m > 2050 and m < 3720 and n > 4140 and n < 4800:
option = self.judgex(x, 2)
else:
option = self.judgex(x, 1)
return [num, option]
if __name__=="__main__":
cardReading = cardReading()
url = cardReading.print_all_file_path("./card");
if len(url) == 0:
Folderpath = filedialog.askdirectory() # 获得选择好的文件夹
url = cardReading.print_all_file_path(Folderpath);
# print(url)
if len(url) > 0:
# for x in range(0,len(url)):
# # print(url[x])
# aaaa = cardReading.reading(url[x], x)
# print(aaaa)
with open('names.csv', 'w', newline='') as csvfile:
fieldnames = list(range(1, 61))
fieldnames.insert(0,'学号')
writer = csv.DictWriter(csvfile, fieldnames=fieldnames)
writer.writeheader() # 注意有写header操作
for x in range(0,len(url)):
# print(url[x])
aaaa = cardReading.reading(url[x], x)
writer.writerow(aaaa)
print(aaaa)
if x == len(url)-1:
print('已全部读取');
for i in range(0,3):
time.sleep(1)
print('即将关闭...%2d.....' % (3-i));
else:
win32api.MessageBox(0, "未选择识别目录", "提醒", win32con.MB_OK)
原始高拍仪图片:
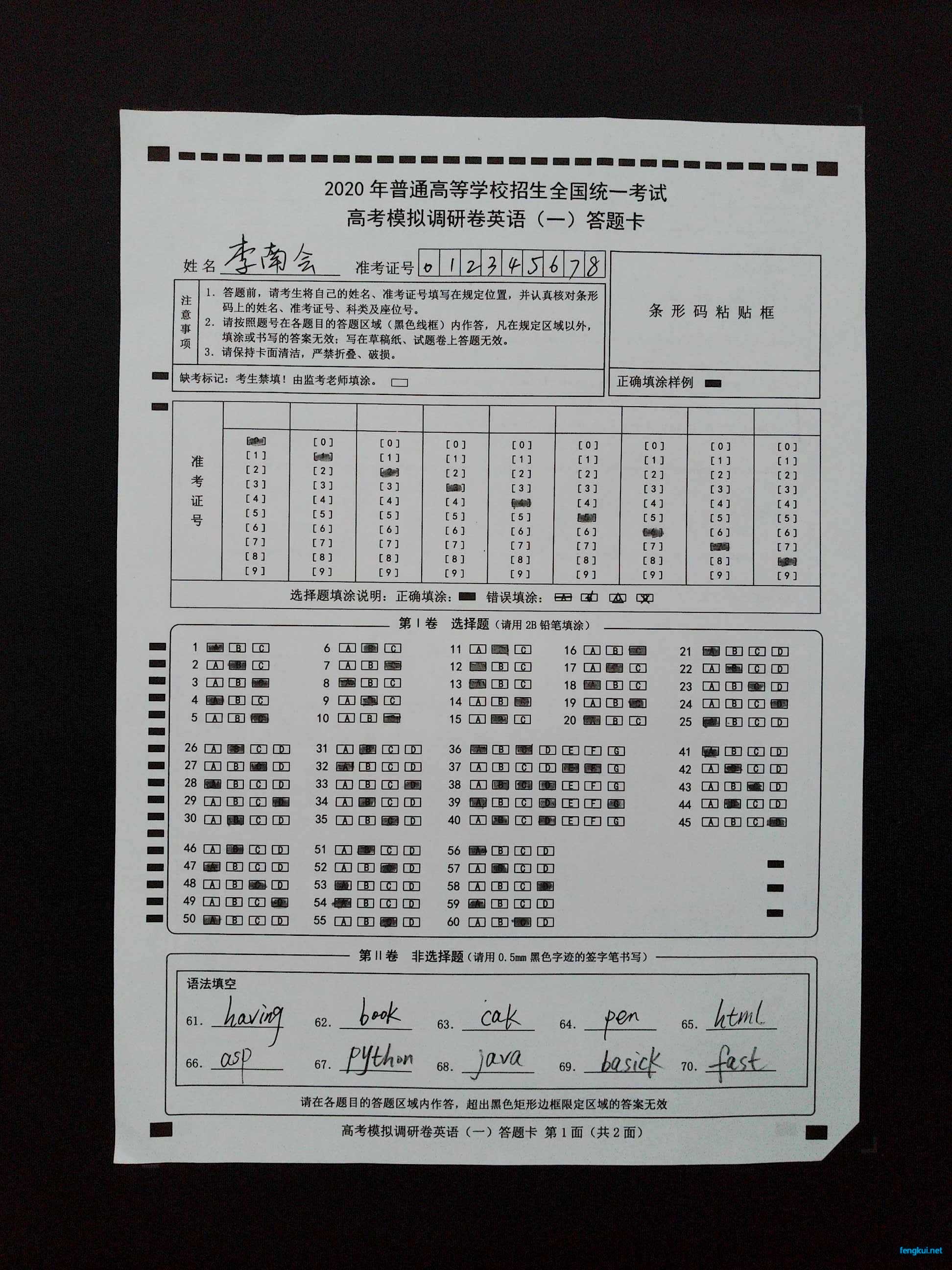
本文为冯奎原创文章,转载无需和我联系,但请注明来自冯奎博客fengkui.net
- 上一篇: opencv+python机读卡识别(初级版)
- 下一篇: PHP图片不变形处理(留白与截取)

请先登录后发表评论
- latest comments
- 总共0条评论
最新评论